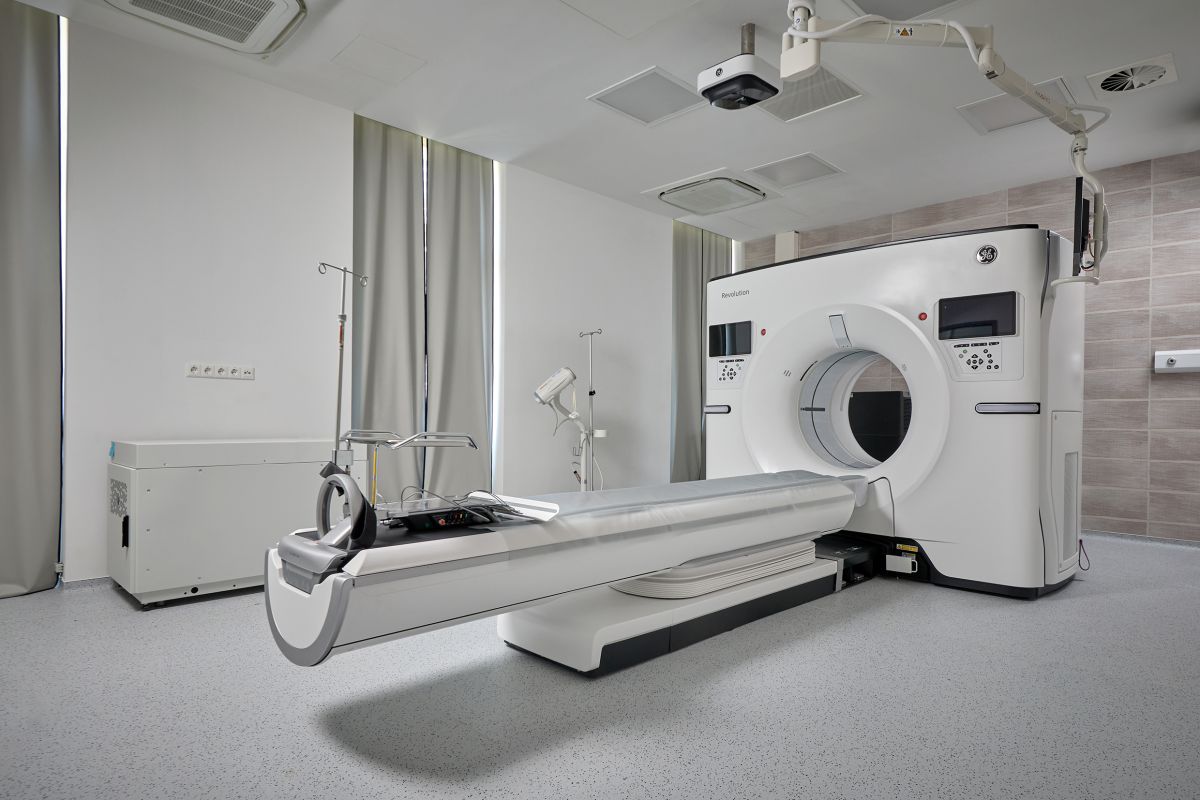
At our clinic – uniquely in Hungary – we perform necessary examinations using the state-of-the-art, 256-slice General Electric CT Revolution Apex, a cutting-edge CT system designed to provide the best possible image quality for every patient with the lowest achievable radiation dose. It is an efficient tool in medical imaging, combining innovation and functionality to meet the demands of modern healthcare professionals. The system is extremely fast, capturing full-body images in seconds, significantly reducing scan time.
What is a CT scan?
A CT (Computed Tomography) scan uses X-rays to create a series of detailed images of specific areas of the body, allowing the visualization of bones and internal organs. CT can provide answers to questions that other diagnostic methods (MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) may not fully address.
During a CT scan, the X-ray tube rotates around the body part being examined, while a detector on the opposite side captures the X-rays passing through the tissues. A computer then processes these signals to create detailed images. Different tissues absorb X-rays differently, and if tissue composition changes due to a pathological process, its X-ray absorption also changes. This makes abnormalities, tumors, organ injuries, bleeding, and inflammation visible on the images.